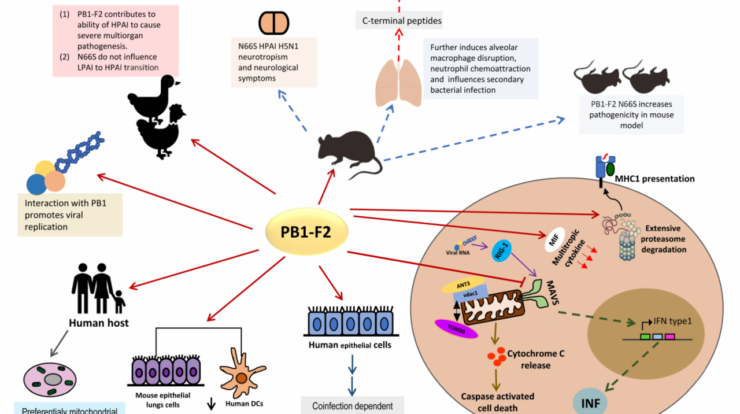
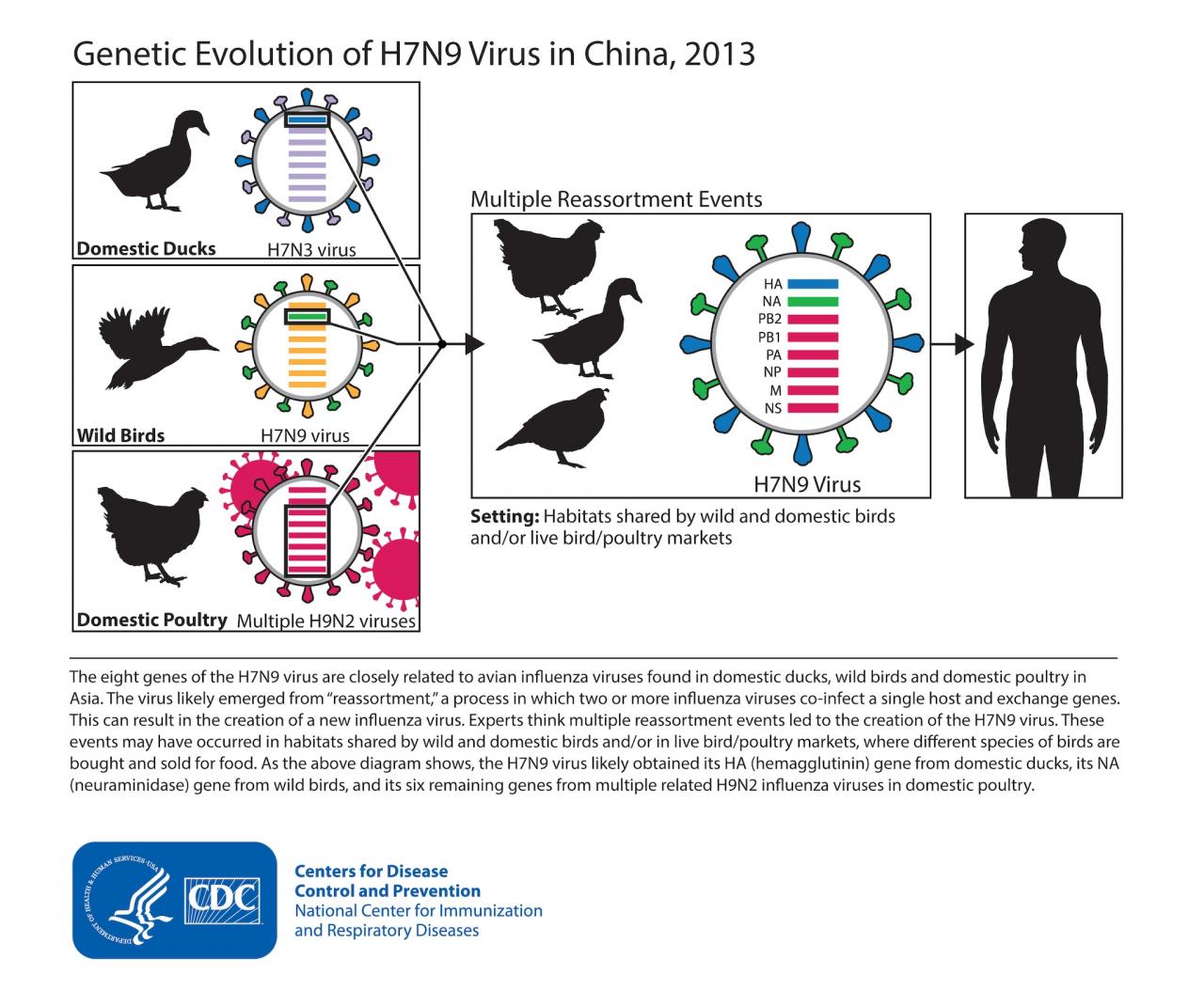
H7N9, a highly pathogenic avian influenza virus, has emerged as a significant public health concern worldwide. This virus has the potential to cause severe respiratory illness in humans, and understanding its transmission, symptoms, and prevention is crucial for mitigating its impact.
H7N9 has primarily been transmitted to humans through direct contact with infected poultry or contaminated environments. The virus can also spread through respiratory droplets when an infected person coughs or sneezes. Factors such as age, underlying health conditions, and exposure to infected birds can influence an individual’s susceptibility to H7N9 infection.
Transmission and Infection
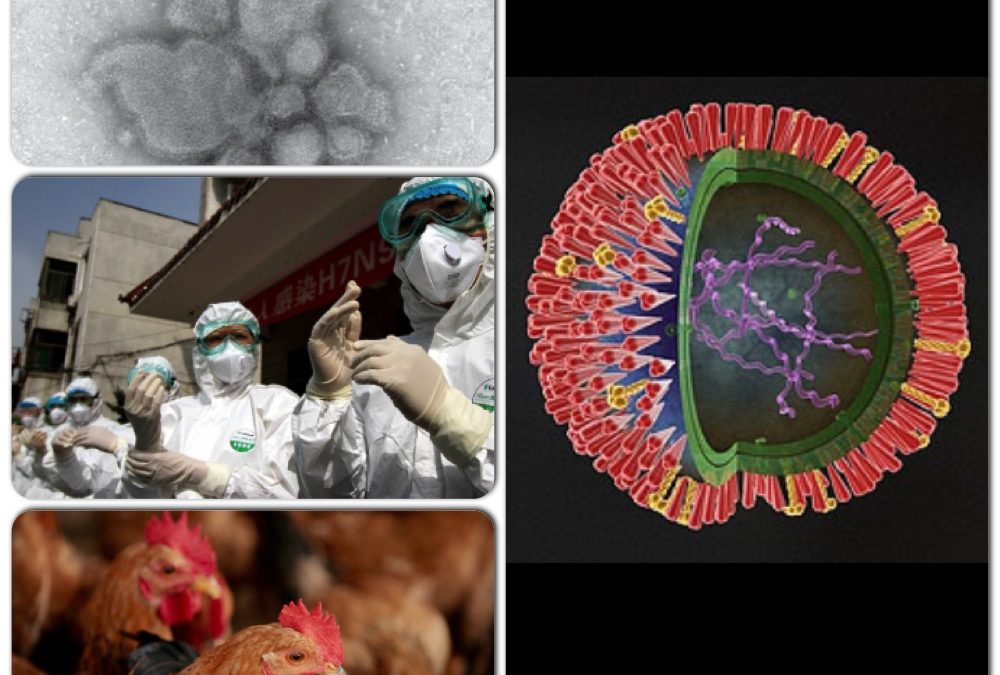
H7N9 virus primarily spreads through direct contact with infected poultry or their secretions, including feces, saliva, and nasal discharge. Human-to-human transmission is rare but has been reported in close-knit communities or healthcare settings.
Factors Contributing to Human Susceptibility, H7n9
- Exposure to infected poultry or contaminated environments
- Weakened immune system due to underlying medical conditions
- Close contact with infected individuals in healthcare settings
Geographical Prevalence
H7N9 outbreaks have been most prevalent in China, with sporadic cases reported in other Asian countries and occasionally in North America and Europe. The virus is endemic in poultry in these regions, contributing to its continued circulation and potential for human infection.
Clinical Manifestations and Symptoms
H7N9 infection can present with a range of symptoms, from mild respiratory illness to severe pneumonia and respiratory failure. Common symptoms include:
- Fever
- Cough
- Shortness of breath
- Muscle aches
- Fatigue
Symptom Severity and Progression
The severity of symptoms can vary widely among infected individuals. Some may experience only mild illness, while others may develop severe respiratory complications. Progression to severe disease is more common in older adults, those with underlying medical conditions, and immunocompromised individuals.
Complications and Long-Term Effects
H7N9 infection can lead to severe complications, including pneumonia, acute respiratory distress syndrome (ARDS), and multi-organ failure. Long-term effects of H7N9 infection are still being studied, but some survivors may experience persistent respiratory problems or other health issues.
Diagnosis and Treatment
Diagnosis
Diagnosis of H7N9 infection is typically made through laboratory testing, such as real-time polymerase chain reaction (RT-PCR) or viral culture. These tests can detect the presence of the virus in respiratory samples.
Treatment
The primary treatment for H7N9 infection is antiviral medications, such as oseltamivir or zanamivir. These medications are most effective when started early in the course of the illness. In severe cases, supportive care, including oxygen therapy and mechanical ventilation, may be necessary.
Importance of Early Diagnosis and Treatment
Early diagnosis and treatment are crucial for improving patient outcomes. Antiviral medications can reduce the severity of symptoms and the risk of complications. Therefore, it is essential for individuals who suspect they may have been exposed to H7N9 to seek medical attention promptly.
Prevention and Control Measures
Public Health Measures
Public health measures to prevent and control H7N9 outbreaks include:
- Surveillance and monitoring of poultry populations
- Vaccination of poultry
- Isolation and quarantine of infected poultry
- Personal protective equipment (PPE) for poultry workers
Vaccination
Vaccination is an important preventive measure for individuals at high risk of H7N9 infection, such as poultry workers, healthcare professionals, and travelers to affected areas.
Personal Hygiene and Infection Control
Personal hygiene and infection control practices, such as handwashing, avoiding contact with sick poultry, and using proper respiratory etiquette, can help reduce the spread of H7N9.
Epidemiology and Surveillance
Epidemiology
H7N9 virus is a zoonotic virus that primarily infects poultry. Human infections are sporadic and typically occur after exposure to infected poultry or their secretions. The incidence of H7N9 infection in humans has varied over time, with outbreaks occurring periodically in different regions.
Surveillance
Surveillance systems are essential for monitoring and tracking H7N9 outbreaks. These systems involve the collection and analysis of data on human and animal infections, poultry populations, and environmental factors.
Importance of Surveillance
Surveillance helps public health authorities identify and respond to outbreaks promptly. It also provides valuable information for understanding the spread and evolution of the virus, which is crucial for developing effective prevention and control strategies.
End of Discussion: H7n9
H7N9 is a serious public health threat that requires ongoing surveillance, research, and preventive measures. By understanding the transmission, symptoms, and prevention of H7N9, individuals and communities can take proactive steps to reduce the risk of infection and its potential consequences.





